Understanding Water-Activated Tape (WAT)
Water-activated tape (WAT), also known as gummed paper tape, is rapidly becoming a cornerstone in the packaging world — and for good reason. Made from kraft paper and a water-activated adhesive, this eco-conscious tape offers unmatched tamper-evident security, strength, and sustainability. It’s been around since the early 1900s, but with today’s emphasis on green packaging, WAT is enjoying a renaissance.
When applied to corrugated boxes, it forms a strong, permanent bond that pressure-sensitive tapes simply can’t match. This reliability is due to the intricate construction layers that come together to create a powerful sealing solution. From high-volume e-commerce operations to artisan packaging, WAT is making waves.
Water-Activated Tape (WAT) Construction Layers
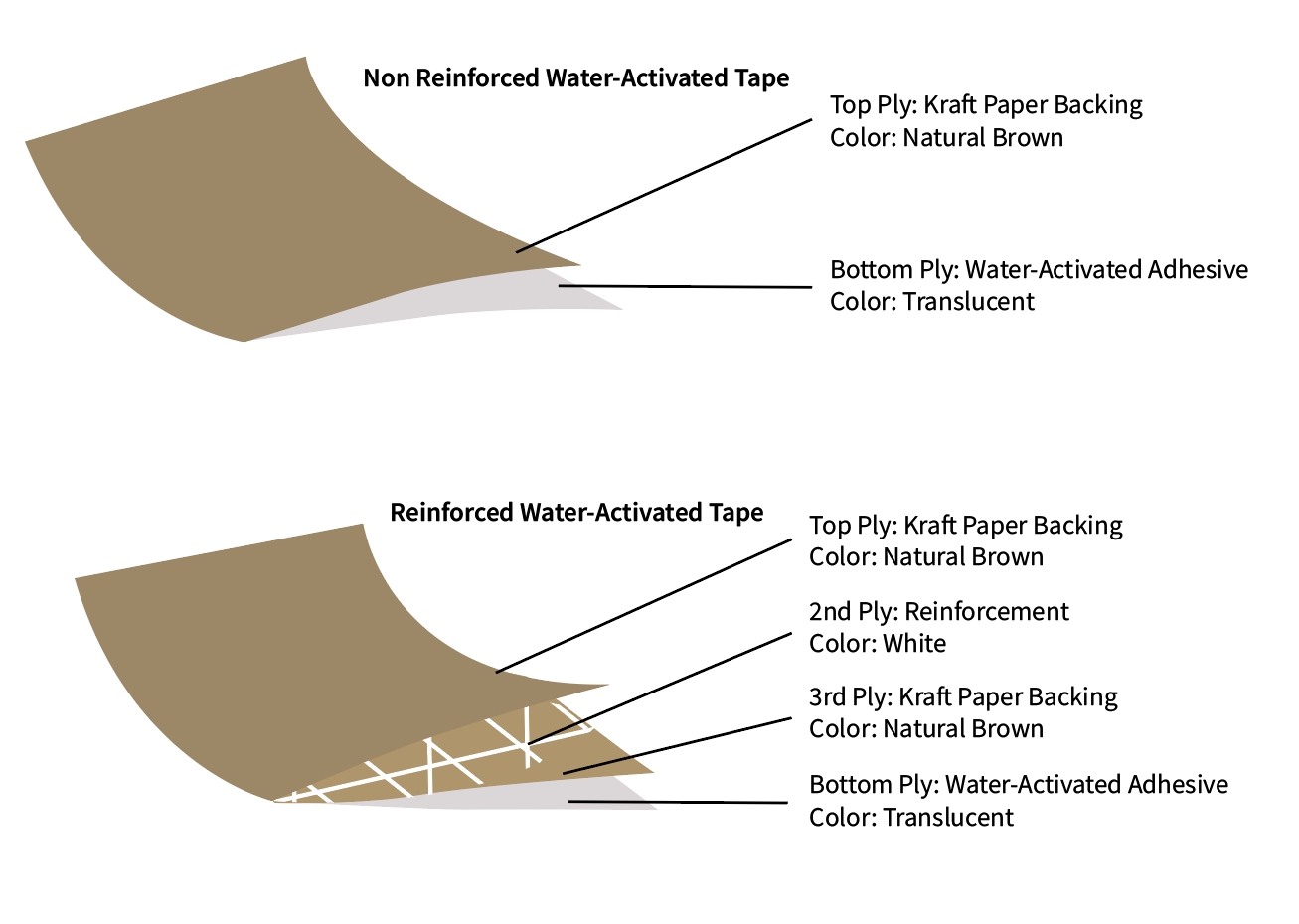
The true magic of WAT lies in its multi-layered construction. While it might look like a simple strip of brown paper to the untrained eye, each layer serves a vital purpose in making WAT effective, efficient, and environmentally friendly.
WAT can usually be divided into two categories, one is Non Reinforced Water Activated Tape and the other is Reinforced Water Activated Tape. Let’s introduce the different Construction Layers of the two types of WAT separately
Ⅰ. Non Reinforced Water-Activated Tape (WAT) – Construction & Material Functions
The Non Reinforced Water-Activated Tape (WAT) is a two-ply paper-based adhesive tape designed primarily for carton sealing. It is composed of a kraft paper backing layer and a water-activated adhesive layer. Each layer plays a critical role in determining the tape’s tensile strength and adhesion performance.
🔹 1. Top Ply: Kraft Paper Backing
-
Color: Natural Brown
-
Material: Virgin or Recycled Kraft Paper
Function:
This layer serves as the structural backbone of the tape. It provides the tape with tensile strength, supports printed branding or handling messages, and contributes to the tape’s durability and visual appeal.
Tensile Strength Characteristics:
-
The tensile strength of WAT is entirely dependent on the kraft paper material:
-
Virgin Pulp Kraft Paper:
-
Made from long, unbroken wood fibers.
-
Offers superior tensile strength and tear resistance.
-
Performs better under high tension and weight.
-
-
Recycled Pulp Kraft Paper:
-
Contains shorter fibers and may include fillers.
-
Has lower tensile strength compared to virgin paper at the same basis weight.
-
-
-
Paper Basis Weight (gsm):
-
Commonly ranges from 60gsm to 90gsm.
-
Higher gsm = thicker paper = stronger tensile strength.
-
For heavy-duty applications, high-gsm virgin kraft paper is preferred.
-
🔹 2. Bottom Ply: Water-Activated Adhesive
-
Color: Translucent
-
Material: Starch-Based Adhesive (Corn or Potato Starch)
Function:
The adhesive layer is activated by water, allowing it to penetrate and bond with the surface fibers of corrugated cartons. This results in a strong, tamper-evident seal that is difficult to remove without damaging the box.
Adhesive Performance Characteristics:
-
Composition:
-
Primarily derived from corn starch or potato starch.
-
Potato starch tends to have slightly better bonding properties due to uniform granule size.
-
-
Coating Weight:
-
The amount of adhesive applied (typically 18–30gsm) directly influences tack and bonding strength.
-
Higher adhesive weight = stronger initial tack and better sealing performance.
-
-
Provides excellent adhesion in both dry and humid conditions.
-
Environmentally friendly and recyclable.
📊 Summary: Performance Comparison
| Layer | Material Type | Key Function | Performance Factors |
|---|---|---|---|
| Top Ply | Virgin / Recycled Kraft Paper | Tensile Strength | Pulp quality, paper basis weight (gsm) |
| Bottom Ply | Water-Activated Starch Adhesive | Adhesion | Starch type, adhesive coat weight (gsm) |
✅ Conclusion
Non Reinforced Water-Activated Tape is an eco-friendly, secure, and cost-effective packaging solution. The kraft paper grade and weight determine its tensile strength, while the adhesive formulation and thickness define its bonding performance. Choosing the right combination ensures optimal performance for various packaging applications.
Ⅱ. Reinforced Water-Activated Tape (WAT) – Construction & Material Functions
Reinforced Water-Activated Tape (WAT) is a premium-grade, high-strength carton sealing solution. It incorporates a multi-layer structure that includes a reinforcement mesh—typically made of fiberglass or an eco-friendly plant-based fiber—to provide superior tensile strength and tamper-evident sealing. This makes it ideal for heavy or high-value shipments.
1. Top Ply: Kraft Paper Backing
-
Color: Natural Brown
-
Material: Virgin or Recycled Kraft Paper
-
Function:
-
Provides structural integrity and printable surface.
-
Acts as the first point of contact and visual branding layer.
-
Helps resist tearing and abrasion.
-
2. Second Ply: Reinforcement Mesh
-
Color: White
-
Material: Typically Fiberglass or Plant-Based Fiber (e.g., Jute or Hemp Yarn)
-
Function:
-
Significantly enhances tensile strength across both length and width.
-
Maintains the tape’s form under tension or impact.
-
Provides resistance against tearing or splitting under heavy loads.
-
Reinforcement Options:
-
Fiberglass Mesh (Standard):
-
Offers extremely high tensile performance.
-
Commonly used in cross-pattern (bi-directional) format.
-
-
Plant-Based Mesh (Eco Option):
-
Made from renewable resources such as jute or hemp.
-
Biodegradable and sustainable, suitable for environmentally conscious brands.
-
Slightly lower tensile strength than fiberglass but suitable for most medium-duty applications.
-
3. Third Ply: Kraft Paper Backing
-
Color: Natural Brown
-
Material: Similar to the top layer
-
Function:
-
Encases the reinforcement for durability and aesthetics.
-
Adds to overall thickness and contributes additional tensile support.
-
4. Bottom Ply: Water-Activated Adhesive
-
Color: Translucent
-
Material: Starch-Based Adhesive (Corn or Potato Starch)
-
Function:
-
When moistened, it penetrates the surface of corrugated cartons and creates a permanent, tamper-evident bond.
-
Provides strong initial tack and long-term hold.
-
Adhesive Performance Factors:
-
Starch Type:
-
Corn starch is widely used for its affordability and good adhesion.
-
Potato starch tends to offer slightly better bonding due to more uniform granule size.
-
-
Coating Weight (gsm):
-
Higher coat weights result in stronger adhesion and better fiber penetration.
-
Typical range: 18–30 gsm.
-
📊 Performance Summary
| Layer | Material | Function | Key Contribution |
|---|---|---|---|
| Top Ply | Kraft Paper | Surface strength, printability | Tensile strength, branding |
| Reinforcement (2nd Ply) | Fiberglass / Plant Fiber | Internal tensile support | Load-bearing capacity |
| Third Ply | Kraft Paper | Encapsulation of reinforcement | Enhanced structure & tear resistance |
| Bottom Ply | Water-Activated Adhesive | Fiber-bonding to carton surface | Strong, permanent adhesion |
✅ Benefits of Reinforced WAT
-
High Tensile Strength – suitable for heavy-duty and high-value shipments.
-
Tamper Evident – breaks the carton surface if removed.
-
Eco-Friendly Options Available – plant-based mesh and recyclable paper.
-
Printable Surface – allows for branding, instructions, or security graphics.
-
Excellent Adhesion – forms a permanent bond when water-activated.
♻️ Sustainability Notes
-
The shift toward plant-based reinforcement materials is gaining traction for companies aiming to reduce their environmental impact.
-
When combined with recycled kraft paper and starch-based adhesives, Reinforced WAT becomes a fully recyclable and biodegradable packaging solution.
FAQs about Water-Activated Tape Construction Layers
What are the main components of water-activated tape?
Water-activated tape is primarily made of kraft paper, starch-based adhesive, and, in some cases, reinforcement fibers such as fiberglass mesh.
Is water-activated tape stronger than regular tape?
Yes, reinforced WAT is significantly stronger and creates a permanent bond that’s more secure than pressure-sensitive tapes.
Can WAT be recycled?
Absolutely. Since WAT is made from paper and natural adhesives, it is fully recyclable and biodegradable.
How does the adhesive in WAT work?
The adhesive is activated by water, allowing it to penetrate the fibers of the box, resulting in a tamper-proof bond.
Is water-activated tape weather-resistant?
It depends. Some WAT comes with a moisture-resistant top coating, while others may need protective packaging in high-humidity environments.
Do you need a dispenser for WAT?
Yes, WAT needs to be applied with a water-activated tape dispenser to moisten the adhesive and apply it properly.
Conclusion: The Future of WAT in Packaging
Water-activated tape represents a perfect intersection of sustainability and strength. As more businesses shift toward eco-friendly practices, WAT’s layered construction becomes even more relevant. Every layer serves a purpose, whether it’s securing shipments, elevating brand presentation, or reducing plastic use. With advances in biodegradable materials and automation-ready dispensers, the future of WAT looks not only promising — it looks essential.